Preventing Damage During Pile Driving with Proper Tip Selection
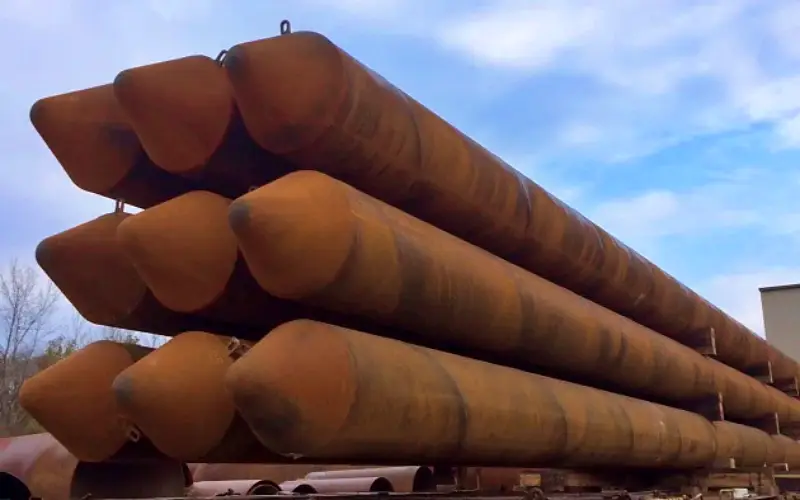


Pile driving places extreme demands on foundation elements as piles are advanced through soils that vary widely in density, composition, and resistance. Damage sustained during driving can reduce structural capacity, complicate quality control, and introduce long-term performance risks. One of the most effective ways to mitigate these issues is proper pile tip selection. Matching tip design to soil conditions and pile type helps protect the pile toe, maintain alignment, and support consistent installation in challenging ground.
Why Pile Damage Occurs During Driving
Impact Energy And Toe Stress
During pile driving, impact energy from the hammer is transferred directly to the pile toe. When resistance increases, stress concentrates at the pile end, particularly in dense soils or bearing layers. Without adequate protection, the pile toe may deform, crack, or experience localized failure. Steel piles are susceptible to mushrooming or distortion, while concrete piles may suffer spalling or crushing near the toe. Proper tip selection reduces these stress concentrations and helps preserve pile geometry throughout installation.
Variable Subsurface Conditions
Most sites exhibit layered soil profiles rather than uniform conditions. Dense sand lenses, gravel layers, cobbles, and construction debris can abruptly increase driving resistance. When piles encounter these materials without appropriate toe protection, damage can occur rapidly. Sudden refusal or uneven resistance can also contribute to pile misalignment, increasing bending stresses along the shaft. Tip design plays a critical role in managing these transitions and maintaining stable driving behavior.
Role of Pile Tips in Damage Prevention
Protecting The Pile Toe
Pile tips act as protective elements that absorb impact forces and shield the pile end from direct contact with abrasive or resistant soils. Their geometry and material properties are designed to resist deformation under repeated blows. By reinforcing the pile toe, tips help prevent loss of cross-section and maintain the integrity of the load path from hammer to bearing strata.
This protection becomes increasingly important as piles are driven deeper and experience cumulative stress from extended driving durations.
Supporting Efficient Penetration
Properly selected pile tips improve penetration by focusing driving energy at the toe in a controlled manner. Reinforced or pointed designs help piles advance through dense layers rather than stalling or deflecting. Improved penetration efficiency reduces the total number of hammer blows required, limiting fatigue-related damage and lowering overall installation stress on the pile.
Matching Tip Design to Ground Conditions
Soft and Cohesive Soils
In soft clays and silts, pile damage risk is generally lower, but tip selection still influences performance. Tips help maintain toe shape, prevent soil intrusion into open-ended piles, and support consistent alignment. Even in low-resistance soils, proper toe protection contributes to predictable driving behavior and uniform load transfer once piles are in service.
Dense Sands and Gravels
Dense sands and gravels present higher abrasion and resistance, increasing the likelihood of toe damage during driving. In these conditions, reinforced pile tips are commonly used to resist wear and deformation. Tip designs intended for abrasive soils help preserve pile geometry and allow piles to reach target embedment depths without compromising structural capacity.
Obstructed or Mixed Fill Conditions
Sites with cobbles, demolition debris, or mixed fill introduce additional uncertainty during pile driving. Robust pile tips reduce the risk of sudden toe damage when encountering unexpected obstructions. They also help maintain straight driving, limiting lateral deflection that can introduce bending stresses into the pile shaft.
Alignment and Load Transfer Considerations
Maintaining Driving Alignment
Pile alignment during driving has a direct impact on structural performance. Off-axis driving increases bending stresses and can exceed design limits, particularly in slender piles. Tip geometry influences how the pile responds when resistance is uneven. Well-designed tips promote stable penetration and reduce lateral wandering, supporting consistent alignment throughout installation.
Preserving Bearing Performance
Damage at the pile toe can reduce effective bearing area and compromise end-bearing capacity. Proper tip selection helps maintain toe geometry, ensuring consistent contact with bearing strata. This is especially critical in applications where axial capacity depends heavily on end bearing rather than shaft resistance.
Installation Quality and Long Term Performance
Reducing Hidden Damage
Not all installation-related damage is visible after driving. Microcracking, localized yielding, or toe deformation can reduce long-term durability without obvious surface indicators. Proper tip selection minimizes the likelihood of these hidden defects, supporting reliable performance over the service life of the foundation.
Improving Predictability During Driving
Consistent tip performance leads to more predictable driving behavior, which simplifies monitoring and quality control. When piles advance smoothly and reach expected depths without abnormal resistance, it becomes easier to verify installation criteria and confirm compliance with design assumptions.
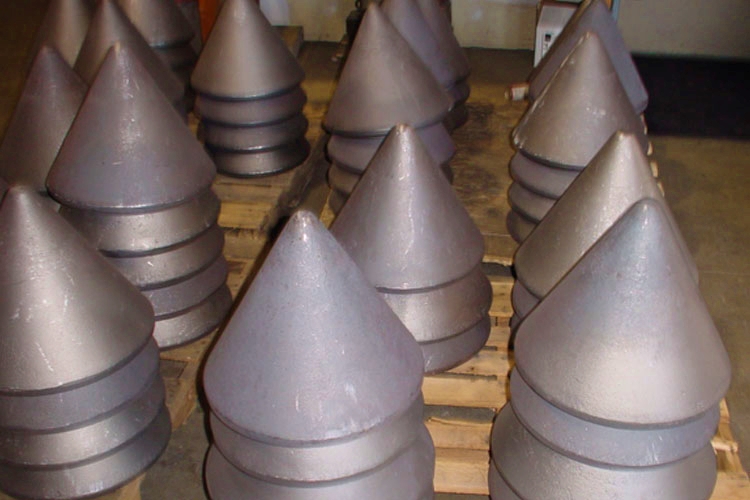

Integrating Tip Selection into Foundation Design
Coordination with Pile Geometry
Tip selection should be coordinated with pile material, wall thickness, and overall length. Longer piles experience greater cumulative driving stress, increasing the importance of toe protection. Integrating tip design early in the foundation planning process helps ensure compatibility across the pile system and reduces installation risk.
Adapting to Project Constraints
Site access, equipment limitations, and environmental conditions all influence tip selection. In marine and waterfront construction, piles may be driven from floating platforms into variable seabed conditions. Tip designs that accommodate these constraints support efficient installation and reduce the risk of damage during driving.
Preventing damage during pile driving requires careful attention to how piles interact with soil resistance and installation forces. Proper tip selection protects pile toes, improves penetration, and reduces stress concentrations that can compromise structural performance. By matching tip design to ground conditions and pile characteristics, project teams can improve installation efficiency and support long-term foundation reliability.
Understanding the role of pile driving accessories for foundation protection remains essential as projects increasingly encounter complex subsurface conditions and tighter performance requirements.
Why is pile tip selection important in pile driving?
Proper pile tips protect the pile toe from deformation, maintain alignment, and preserve load-carrying capacity.
How do pile tips improve penetration in dense or obstructed soils?
Pile tips focus driving energy at the toe, allowing piles to advance efficiently through resistant layers without stalling or bending.

















