Reducing Noise and Vibrations for Pile Driving Applications


View the complete article here.
As the global volume of construction projects continues to escalate, mitigating noise and vibration in pile driving operations is becoming more important than ever.
In response, contractors and other industry professionals have devised innovative methods to reduce the potential disruption caused to surrounding environments and communities. For any contractors utilizing pile driving operations in their projects, understanding these methods are paramount to avoid potential project delays, violations, negative effects on the environment, and other negative consequences.
In this guide, we’re going to cover the different noise and vibration mitigation techniques available, technological advancement, scenarios where noise and vibration is likely to be an issue, as well as regulations and standards.
Noise and Vibration Mitigation Techniques in Pile Driving
Over the years, the pile driving industry has developed innovative methods to curb the intensity of noise and vibrations in pile driving applications. The primary methods include…
Vibratory Hammers
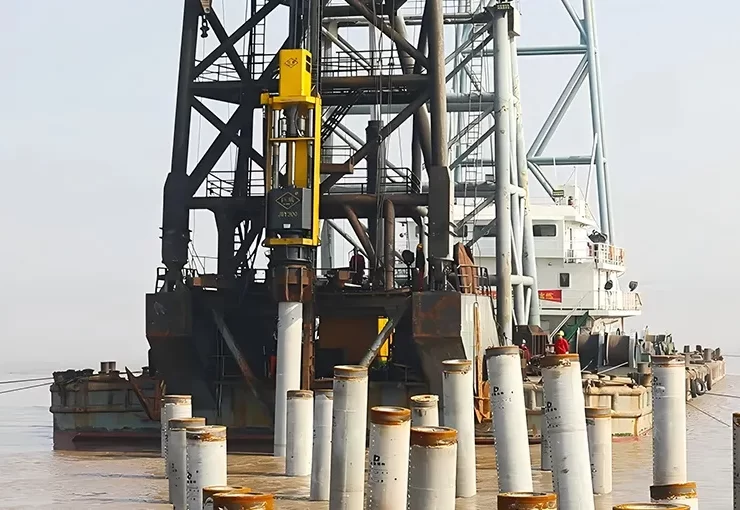
Vibratory pile drivers have become a preferred choice in the construction industry due to their relatively low noise and vibration outputs. Vibratory hammers utilize high-frequency vibratory motions to reduce the friction between the pile and the soil—aiding in driving the pile into the ground with less force and disturbance compared to conventional impact pile driving. This reduction in force results in a significant decrease in noise and vibrations—making it suitable for projects in residential areas or near sensitive structures. Furthermore, vibratory hammers are typically faster than impact hammers—providing an added advantage of reducing the overall duration of pile driving operations and, hence, the time during which noise is generated.
Hydraulic Pressing
Known for its almost silent operation, hydraulic pressing is a method in which piles are pressed into the ground using a hydraulic jack. While this technique may take more time compared to other methods, it offers a virtually noiseless and vibration-free operation. This makes it an excellent choice for construction in sensitive areas such as near hospitals, schools, or historical structures. The gradual and controlled process of hydraulic pressing offers precision and minimizes the risk of damage to nearby structures—a concern often associated with conventional pile driving.
Screw Piling
Another innovative method that reduces the noise and vibration levels is screw piling. In this method, piles designed with a helical blade are rotated or “screwed” into the ground—eliminating the need for intense hammering. The rotation action causes the soil to be displaced rather than compacted—leading to less ground vibration. Screw piles can also be installed rapidly—reducing the time frame during which noise and vibration might disrupt nearby activities. Their ease of installation and removal—combined with their low environmental impact—makes them an attractive choice for temporary or permanent installations in noise-sensitive areas.
Sound Barriers and Shields
In addition to the pile driving techniques mentioned, construction sites can also utilize sound barriers or shields to contain and absorb the noise within the site itself. These barriers—made of dense materials—act as physical obstructions that can prevent the propagation of noise to surrounding areas. Sound barriers and shields can be strategically positioned around the pile driving area or the entire construction site—depending on the site’s layout and the proximity of noise-sensitive receptors. Combining sound barriers with low-noise pile driving techniques can further minimize the noise impact on nearby communities—enabling construction in heavily populated or noise-sensitive areas.
Of course, each of these techniques and practices brings unique advantages (and disadvantages) to the table. For this reason, it’s imperative to have a firm understanding of each before commencing pile driving operations.
Technological Advancements Reducing Noise and Vibration
The days where pile driving was simply a matter of brute force are gone. The current generation of pile driving equipment is an ideal blend of power and precision—incorporating various technological advancements to minimize noise and vibrations. The emphasis today is—arguably—as much on smart, sustainable operations as it is on the foundational strength and integrity of the structures being erected.
Variable Eccentric Moment Technology
One significant innovation that has contributed to reducing noise and vibrations in modern pile driving operations is Variable Eccentric Moment (VEM) technology. Standard in most modern vibratory hammers, VEM allows the equipment to gradually ramp up and down the vibratory force. This technology reduces sudden impacts—thereby lowering the peak noise and vibration levels that can be particularly disruptive. In essence, VEM technology provides a soft-start and soft-stop mechanism for the vibratory forces—allowing for a smoother and quieter operation. VEM technology is ideal for construction projects adjacent to sensitive structures like historical buildings, hospitals, or schools. VEM’s gradual ramping of vibratory force reduces the risk of damage due to vibrations—ensuring the structural integrity of these existing buildings is maintained.
Real-Time Monitoring Systems
Another critical component of modern pile driving operations is real-time monitoring systems. These advanced systems provide immediate, accurate feedback about noise and vibration levels during pile driving operations. This live data stream allows operators to adjust the piling process instantly based on the monitored levels—ensuring that they remain within permissible limits. Such precise control over pile driving operations significantly reduces the risk of violating noise and vibration regulations and helps maintain good relations with local communities and authorities.
Advanced Materials and Design
Advancements aren’t limited to just the equipment. The piles themselves have seen significant developments. Today, piles are designed with materials optimized for noise and vibration reduction. For instance, some piles are built with composite materials that absorb and dampen vibrations. The design of the piles can also influence the level of noise and vibrations generated during pile driving. For example, piles with a tapered end can be driven into the ground with less resistance—reducing the impact force needed and consequently the noise and vibration generated.
Needless to say, pile driving technology has evolved quite a bit since the Romans were utilizing it two thousand years ago. Modern pile driving is a sophisticated process that leverages the latest technology to minimize environmental and community impact. These advancements ensure that pile driving operations can carry on efficiently—even in sensitive areas—without compromising the project’s structural integrity or community relations.

Scenarios Where Pile Driving Noise and Vibration May be an Issue
Here are some of the most common scenarios where pile driving noise and vibration may be an issue…
Urban Residential Construction
Consider a high-rise residential project located in the heart of a bustling city—surrounded by existing residential and commercial buildings. In this scenario, utilizing vibratory hammers for pile driving can minimize noise and vibration disturbances—allowing construction to proceed without disrupting the daily life of nearby residents. In addition, the use of sound barriers could further contain the construction noise—keeping the urban peace intact.
Historical Site Renovation
Imagine a renovation project happening at or near a historical site that houses ancient, delicate structures. Needless to say, a significant level of care required in these circumstances is crucial. Employing low-impact pile driving method—such as hydraulic pressing—ensures the stability and integrity of the historic structures, while the necessary foundation work is completed. The slow, silent operation of hydraulic pressing is an ideal choice for such sensitive environments.
Hospital Construction
During the construction of a hospital, it’s paramount to maintain a serene environment—as noise disruptions can negatively affect patient recovery. In this case, using a combination of low-noise pile driving methods—such as screw piling—and implementing noise reduction strategies—like sound barriers or shields—can help maintain a peaceful atmosphere. Regular monitoring and adjusting operations based on real-time noise data can also ensure a quieter construction process for hospitals.
School Construction
With the construction of a school in a residential neighborhood, the schedule could be timed to align pile driving activities with school hours to minimize disturbance. Employing techniques like soft-start—where energy input is increased gradually—can also help reduce sudden noise and vibrations that might disrupt learning activities.
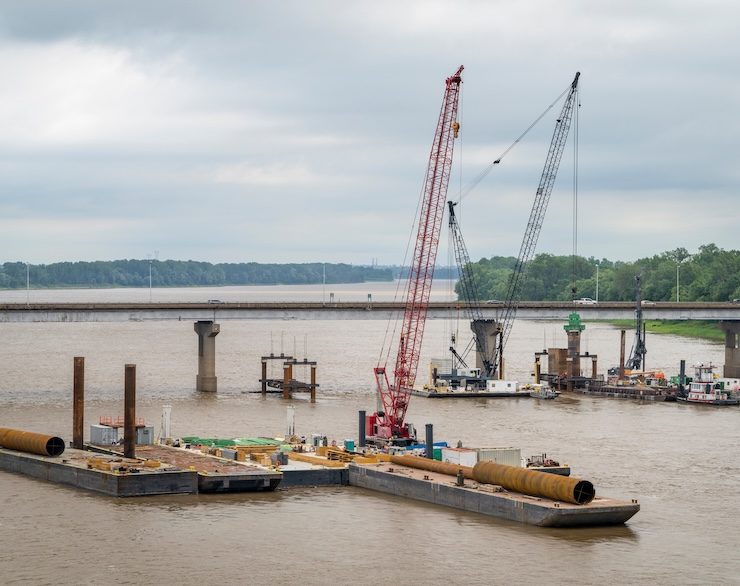
Marine Construction
Consider wildlife habitats during marine construction projects—like bridge construction, for example. In these scenarios, it’s important to ensure that construction noise doesn’t disturb the animals. Using low noise and vibration pile driving techniques—like screw piling or hydraulic pressing—along with sound barriers—can help minimize the disturbance to wildlife.
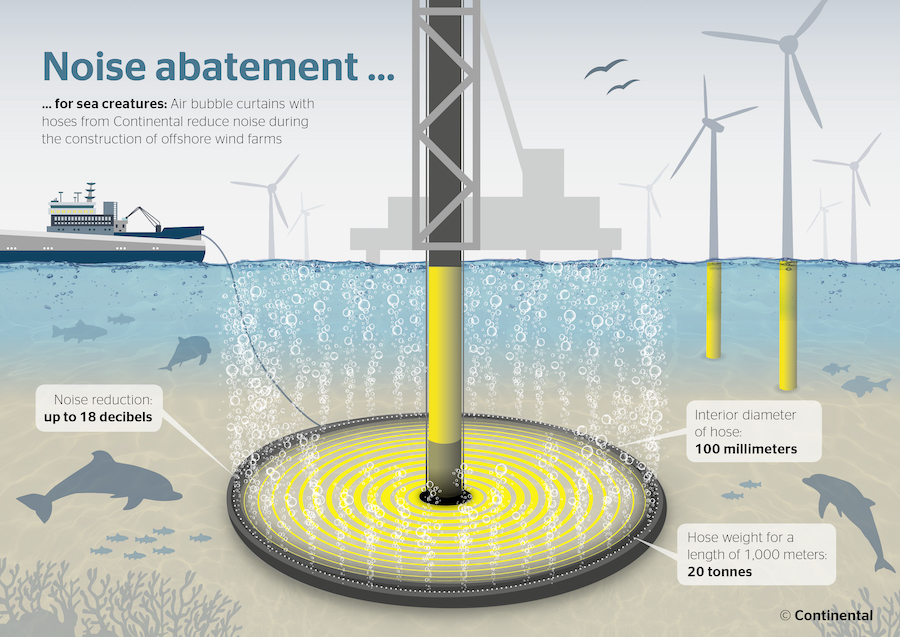
In the case of a new offshore wind farm project—where piles need to be driven underwater—the need for noise reduction techniques is even more critical due to their potential impact on marine life. Here, Continental’s Big Bubble Curtain Hose could play an essential role. This technology creates a curtain of bubbles in the water that dampens the noise and vibration caused by underwater pile driving—thereby protecting various marine species. In addition, the usage of low noise and vibration pile driving methods like hydraulic pressing or rotary drilling can also significantly reduce the impact on the marine environment.
Regulations and Standards for Noise and Vibration in Pile Driving in the United States
In the United States, construction activities—including pile driving—are subject to a plethora of regulations to control noise and vibrations. These regulations are mostly local—with specific noise ordinances in cities or counties. For example, many urban areas impose restrictions on the times during which pile driving can occur to limit noise disruption for residents.
Furthermore, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates legal limits on noise exposure in the workplace. Regulations stipulate that exposure to average noise levels of 85 decibels or higher over an 8-hour work shift requires the implementation of a hearing conservation program. These programs ensure the auditory health of construction workers—often overlooked amidst other safety measures.
For vibrations, the U.S. Bureau of Mines provides guideline values for ground vibration to prevent structural damage. These guidelines become significantly relevant for pile driving near sensitive structures—helping to prevent inadvertent damage.
Conclusion
Techniques such as the use of vibratory hammers, hydraulic pressing, screw piling, and sound barriers have emerged as viable solutions to issues caused by pile driving noise and vibration.
Further enhancing these efforts are technological innovations like variable eccentric moment technology, real-time monitoring systems, and the usage of advanced materials. These contribute not only to the efficiency and effectiveness of construction but also significantly decrease the disruption caused to surrounding environments.
These contributions reflect a deep-seated commitment to responsible construction and underscore the importance of respecting both the stability of the community and the structural integrity of our projects. As we move forward, it is essential to continue exploring and integrating these advancements.
View the complete article here.
How do vibratory hammers contribute to reducing noise and vibrations in pile driving?
Vibratory hammers use high-frequency motions to minimize friction, resulting in lower force and disturbance during pile driving, significantly reducing noise and vibrations.
What are some scenarios where pile driving noise and vibration could be problematic, and how can they be addressed?
Scenarios like urban residential construction, historical site renovation, hospital or school construction, and marine projects may require low-noise methods such as vibratory hammers, hydraulic pressing, or sound barriers to minimize disruptions and adhere to regulations.

















